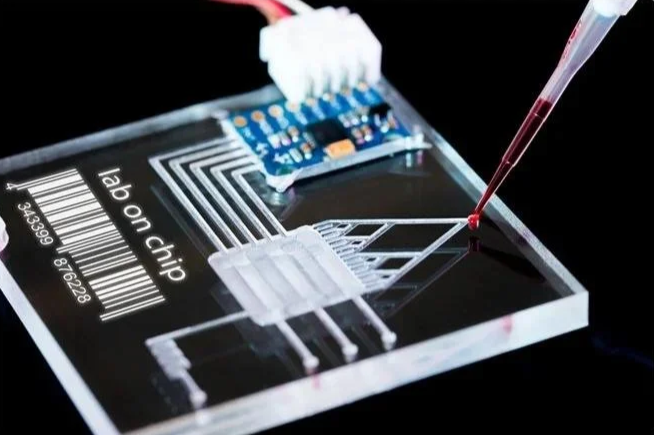
Lab-on-a-chip
Lab-on-a-chip is the physical and functional backbone of the microfluidic system you use to produce liposomal Doxorubicin.
It is a miniaturised manufacturing environment where fluid handling, mixing, solvent exchange, and nanoparticle self-assembly occur inside precisely engineered micro-channels.
The chip fixes flow geometry, shear profiles, and diffusion conditions, which eliminates batch variability and forces every liposome to form under identical physical constraints.
This drives uniform particle size, high encapsulation efficiency, and reproducible pH-responsive behaviour.
In short: it replaces bulk, inconsistent chemistry with controlled, continuous, machine-defined nanoparticle engineering.